2022-06-04
Description
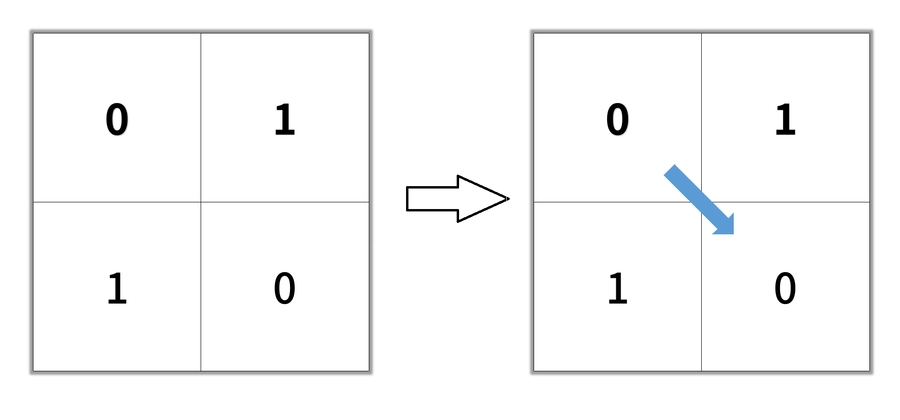
Input: grid = [[0,1],[1,0]]
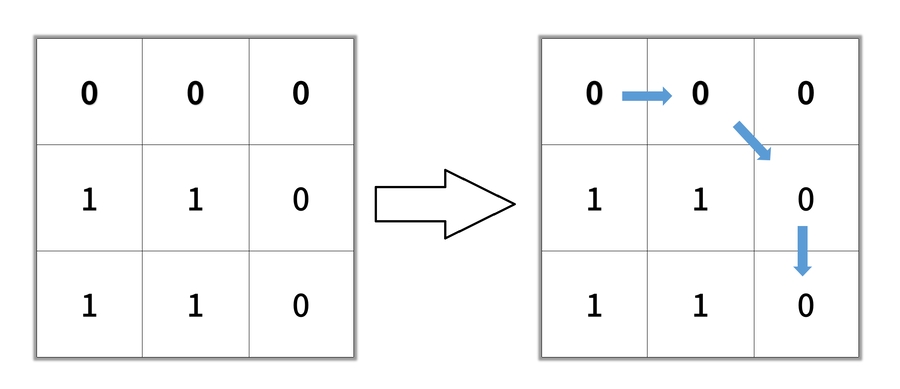
Output: 2Input: grid = [[0,0,0],[1,1,0],[1,1,0]]
Output: 4Solution
Approach #0
Description
Solution
Approach #0: BFS
Approach #1: DFS
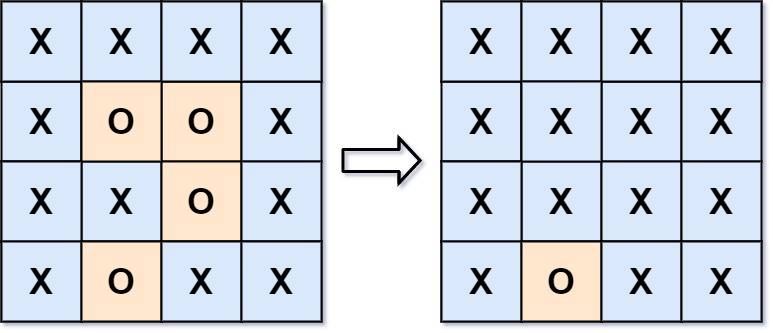
Description
Solution
Approach #0: DFS
Approach #1: BFS
Last updated