2022-05-21
Description
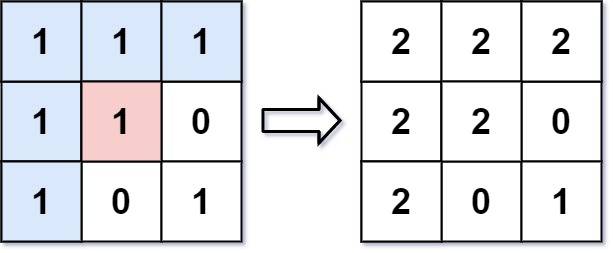
Input: image = [[1,1,1],[1,1,0],[1,0,1]], sr = 1, sc = 1, newColor = 2
Output: [[2,2,2],[2,2,0],[2,0,1]]
Explanation: From the center of the image with position (sr, sc) = (1, 1) (i.e., the red pixel), all pixels connected by a path of the same color as the starting pixel (i.e., the blue pixels) are colored with the new color.
Note the bottom corner is not colored 2, because it is not 4-directionally connected to the starting pixel.Input: image = [[0,0,0],[0,0,0]], sr = 0, sc = 0, newColor = 2
Output: [[2,2,2],[2,2,2]]Solution
Approach #0: DFS
Approach #1: BFS
Description
Solution
Approach #0: BFS
Approach #1: DFS (Recursive)
Approach #2: DFS + Stack (Iterative)
Last updated